During last months I got more and more interested in Web Analytics. Firstly, thanks to my job and secondly it drove me there because of the close connection to online marketing (which is my another interest). Once you need to evaluate your online marketing efforts then analysis based on online data (sure you can also import other data then those stored by Google) is a must. Well, web analytics will be becoming more and more important in the online world. Not just for owners of e-commerce sites or online software providers but it might also catch interest of website owners in terms of improving their websites with help of available data about their sites.
The most common thing you do when you decided to start tracking your website in Google Analytics (GA) is to create a view. I do not count the process before (creating an account and properties there). Once you did steps before, then choose the property (maybe if you have more sites you want to track it would be good to group them in different properties according the same key they share, e.g. properties based different regions etc.) in which you want to track your site. Moreover, you click create a view (depicted on the picture below)
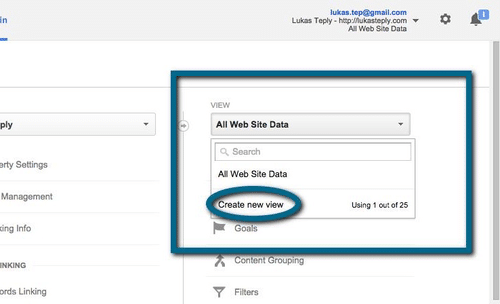
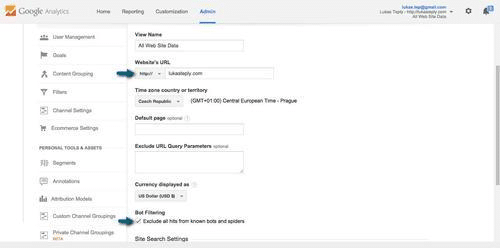
Then you have to follow the basic steps of creating a view such as name of the view and set your time zone. In the next step you go to view settings and specify the website’s URL, currency, the URL query parameters you want to exclude or you can turn on site search tracking. It is good to check a box “Exclude All Hits From Known Bots and Spiders.” It simply excludes all known bots and spiders from AB/ABC International Spiders & Bots List.
User management & Goals
Furthermore, apart from the basic settings you can set goals (e.g. you want to see how many people register to your newsletter), add users to access you view in GA (and don’t forget to grant them specific rights (read&analyse, collaborate, edit and add users) too!). The important tab here is “Filters.” I really recommend you to add at least the filter excluding your or company IPs (you figure it out really simply on http://www.whatismyip.com/).
Filters
It is really easy to set it up. You just add a new filter, name it and then choose the custom one and check a box “Exclude”. You need to find IP address (the easiest way is to look it up) and finally you have to write the IP address. Maybe you noticed the “\” character (backslash) in front of “.” The answer for that is easy. Since the backlash character turns any special character into a literal one. More about regular expressions can be found here.
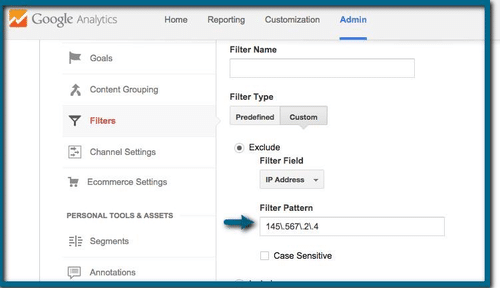
Another filter could include hostname of your site. That enables to view your hostname in the reports.
Content Grouping
“Content grouping” could be also helpful in way you want to group a content of your site into a structure. E.g. you track an ecommerce site and you want to compare different groups of products (pants x skirts, shirts x t-shirts etc.). That is the way how content grouping works. It helps you with comparing statistics of different groups.
Ecommerce settings
For e-commerce tracking it is important to turn on the e-commerce tracking. Simply, go to the E-commerce Settings tab. And then turn on “Enable Ecommerce.” However, this is just a beginning for tracking your e-commerce site. You have to do other things in order to get data from your online store (for instance you need to add a data layer etc.).
Overall, if you read the article to this line then you got a quick overview of creating a view in Google Analytics and its basic settings. Do not forget about the importance of web analysis. It helps you in making decisions such as re-designing your site, analysing your e-commerce site or evaluating your marketing campaign. It is definitely worth a try.
Sources: Lunametrics, Google, WhatismyIP

Marketing Makers LLC
Evergreen, Colorado